Valvular heart disease is a serious condition that affects the valves of the heart, which are responsible for controlling the flow of blood in and out of the heart.
When these valves become damaged or diseased, it can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, including shortness of breath, chest pain, and heart failure.
Valvular heart disease is a significant health concern, and it is important to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect that you may be affected.
With the right treatment and care, many people with valvular heart disease are able to manage their condition and lead full and healthy lives.
-
The heart valves play a crucial role in the proper functioning of the heart. There are four main valves in the heart: the mitral valve, the tricuspid valve, the aortic valve, and the pulmonary valve. These valves open and close in a specific sequence to control the flow of blood in and out of the heart.
The mitral valve and tricuspid valve are located between the atria and ventricles, while the aortic valve and pulmonary valve are located at the exit of the ventricles.
When the heart contracts, the valves open to allow blood to flow through, and then close to prevent backflow. This constant opening and closing of the valves is what keeps blood flowing in the right direction and ensures that the heart can function effectively.
Valvular heart disease can occur when these valves become damaged or diseased, leading to a range of symptoms and complications.
-
Valvular heart disease is a condition where the valves of the heart become damaged or diseased. The valves control the flow of blood in and out of the heart. When they are not functioning properly, it can lead to a variety of problems either due to backward leakage of blood, or obstruction to the forward flow of blood.
-
There are many possible causes of valvular heart disease, including age-related wear and tear, infections, and certain medical conditions such as rheumatic fever or connective tissue disorders. Some people may also be born with abnormal valves.
-
The symptoms of valvular heart disease can vary depending on the severity of the condition and which valve is affected. Some common symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain or discomfort, fatigue, lightheadedness, and palpitations.
-
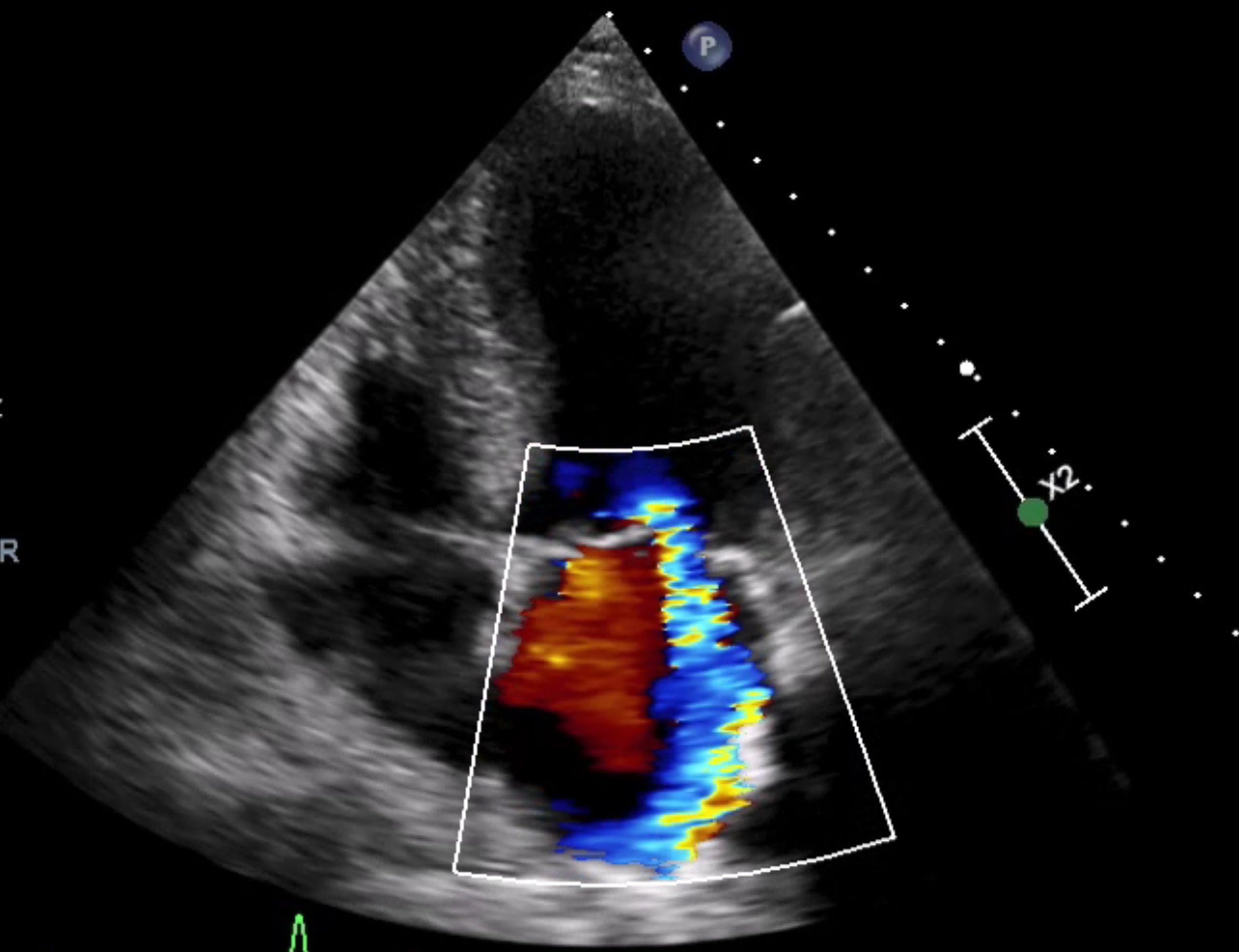
Valvular heart disease is usually diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, imaging tests such as echocardiograms, transoesophageal echocardiograms, or CT scans. Other diagnostic tests such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) can assist too.
-
The treatment for valvular heart disease depends on the severity of the condition and which valve is affected. Some people do not need any treatment at all, while others may need medication, surgery or other interventions.
Recent advances in technology has allowed minimally invasive treatment for many of these conditions, and it is important that your cardiologist is aware of the different approaches and which is appropriate for you.
-
There are several things you can do to reduce your risk of developing valvular heart disease, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing any underlying medical conditions, and seeking prompt medical care for any symptoms you may experience.
If you have been diagnosed with valvular heart disease or are concerned that you may be at risk, it is important to speak with a qualified cardiologist. Dr Ee-May Chia is an expert cardiologist with years of experience in treating patients with valvular heart disease. Importantly, her understanding of the different imaging modalities allows her to recommend the best treatment available for your condition. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and learn more about how we can help you manage this condition.
